-
Lipid Bilayered Nanoparticles
Extracellular vesicles are cell-derived membranous vesicles, comprising exosomes and microvesicles. We mainly focus on a subgroup of EVs sized 30-150 nm (Exosomes or small EVs). They contain various important biological macromolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, etc.

-
Natural Intercellular Messengers
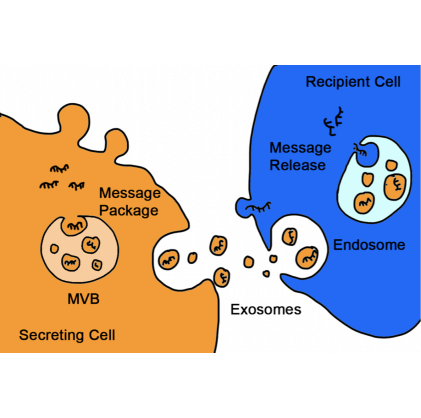
Almost all types of cells can secret exosomes into extracellular environment. Exosomes function as natural messengers to transfer biological contents, enabling crosstalk between cells and changing the behavior of the recipient cells.
-
Programmable delivery vehicles
The biogenesis of exosome is a delicate process that governed by specific cellular mechanisms, and various biological active molecules are sorted into the exosomes. Therefore, exosomes could be engineered by specific designs, enabling them as effective drug delivery vehicles with multifunctionality.